
Introduction to The Chemistry and History of NN-DMT
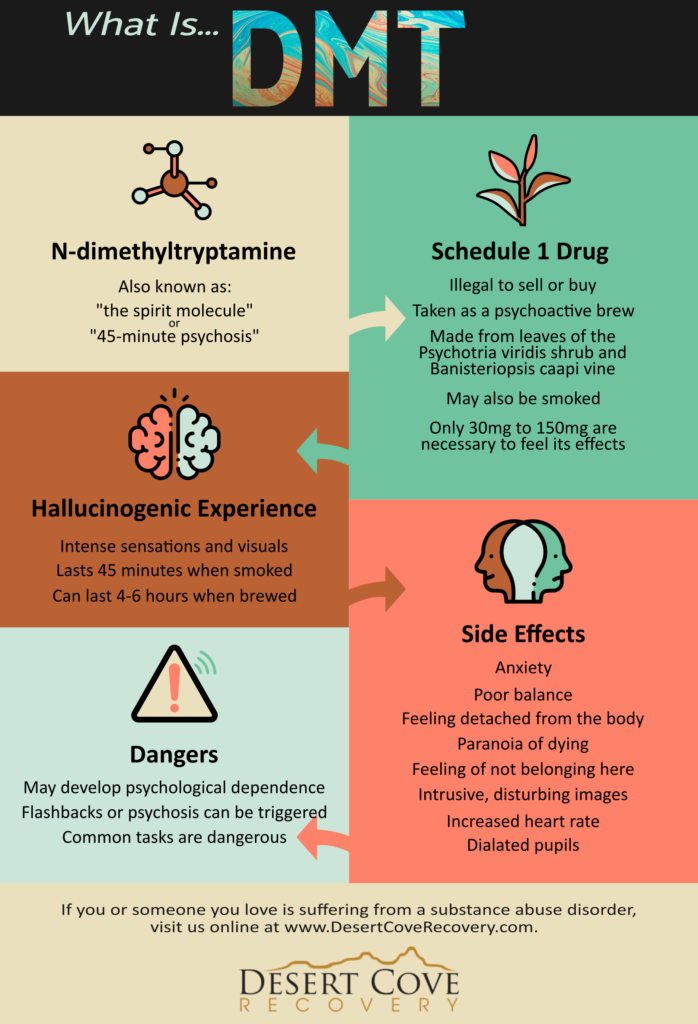
N,N-DMT, or N,N-Dimethyltryptamine, is one of the most powerful psychedelic substances known to science. Found in plants, animals, and even the human brain, DMT has been used in spiritual ceremonies for centuries. But what exactly is this molecule — and why are researchers and psychonauts in Texas so fascinated by it?
What Is NN-DMT?
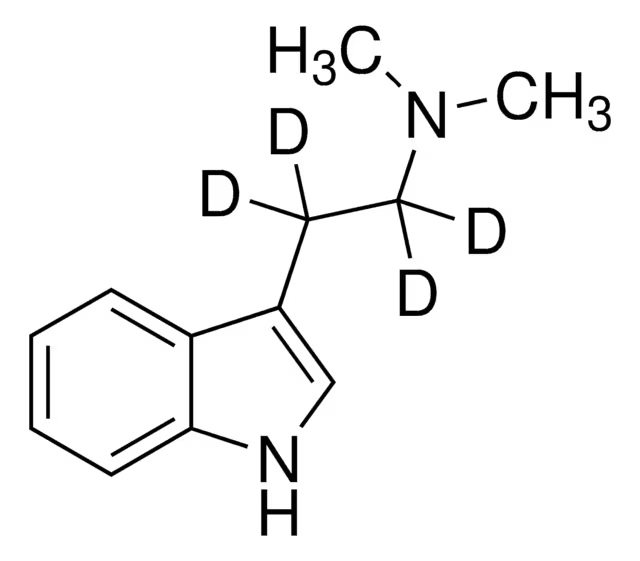
Chemically, N,N-DMT is a tryptamine alkaloid, structurally similar to serotonin and melatonin. It’s naturally produced in various plant species like Psychotria viridis and Mimosa hostilis, and it’s often extracted for personal or spiritual use.
When smoked or vaporized, the effects are intense and fast-acting — often referred to as a “breakthrough” experience.
A Brief History of DMT Use
DMT’s use dates back thousands of years. Indigenous Amazonian tribes consumed it in the form of Ayahuasca, a ceremonial brew. In the West, it caught the attention of chemists in the 20th century. Dr. Rick Strassman’s 1990s research popularized the idea that DMT may play a role in near-death experiences and dreams.
In modern-day Texas, growing interest in alternative spirituality and psychedelics has put DMT on the radar of many seeking deeper consciousness.
The DMT Molecule and Brain Chemistry
Some researchers speculate that the pineal gland may produce small amounts of DMT. While unproven, the theory has fueled spiritual interpretations. What is certain: DMT closely mimics neurotransmitters in the brain, allowing it to bind to serotonin receptors and launch users into an otherworldly state.
Legal and Scientific Interest in Texas
Although DMT remains a Schedule I substance in the U.S., there’s growing pressure to re-evaluate its legal status — especially as psychedelic research centers emerge in states like Oregon and California. Texas has seen increased public curiosity, with underground DMT retreats and private ceremonies becoming more common.
More on The Chemistry and History of NN-DMT
N,N-DMT is more than a drug — it’s a gateway to altered states that have fascinated humans for generations. From ancient rituals to cutting-edge neuroscience, its story is far from over. If you’re in Texas and exploring psychedelics for spiritual or research purposes, understanding the roots and chemistry of DMT is the first step on a deeper journey.
Want to explore more about DMT products, retreats, or research chemicals? Visit DMTNearMe.store — your trusted source for psychedelic education and high-quality products in the U.S.
N,N-Dimethyltryptamine (DMT) is a psychedelic compound found naturally in many plants and animals, and also synthesized by the human body. It’s a serotonergic hallucinogen and a research chemical. Historically, DMT has been used in indigenous Amazonian shamanic practices, particularly as a key component of the ayahuasca brew. Chemically, DMT is a tryptamine, structurally related to other psychedelic compounds like psilocin.
Chemistry:
DMT’s chemical name is N,N-dimethyltryptamine, indicating the presence of two methyl groups attached to the nitrogen atom in the indolethylamine structure.
It belongs to the tryptamine class of compounds, which share a common indole ring structure.
DMT is a close relative of other psychedelic compounds like 5-MeO-DMT (5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine) and bufotenin (5-OH-DMT).
The structural similarity to psilocin, the active compound in psilocybin mushrooms, is noteworthy.
History:
DMT is found naturally in various plant species, including Mimosa tenuiflora, Diplopterys cabrerana, and Psychotria viridis.
It’s a primary psychoactive component in some plants and a minor component in others.
DMT-containing plants have been traditionally used in Amazonian shamanic rituals, notably in ayahuasca.
Ayahuasca, a brew used in shamanic practices, often includes DMT-containing plants.
Some yopo and vilca snuff preparations, made from Anadenanthera peregrina and Anadenanthera colubrina also contain DMT as a minor alkaloid.
5-MeO-DMT, a related compound, was first isolated from natural sources in 1959 and reported to be hallucinogenic in 1970.
